
Sewing in the garment industry is the main profitable section. Sewing Room Management in the Apparel industry is so important factor. Sewing is a craft that involves stitching fabrics or other materials together by using a needle and thread by hand or with a machine. After receiving the cut garment parts from the cutting section, they are sewn sequentially to make a garment.
Some pre-required factors are checked before going to bulk production. They are:
- All the required machines are available or not
- Is the workforce optimum or not
- The line is arranged according to the given layout
- If the cutting parts are numbered
- The selection of needle sizes is done or not, etc.
Discussing points of this article:
- To know the sewing company profile.
- Gather knowledge about the layout of different garments.
- To know about the different sewing machine and their working process.
- Getting knowledge about the defects and remedies of garments.
- To know about different types of needles used in the garments industry.
Quality Assurance organogram of sewing floor:
The quality assurance department of a sewing floor is given step by step.
GM Quality Assurance
⇓
Manager Quality assurance
⇓
Asst./Deputy Manager
⇓
Sr. Officer/ Officer
⇓
The Quality Controller
⇓
Quality Supervisor
⇓
The Quality Inspector
Flow chart of Sewing in the garment industry:
The flow chart of the sewing floor is below step by step
Preproduction meeting
⇓
Cutting quality
⇓
Item conformation
⇓
Input
⇓
layout
⇓
In-process quality control
⇓
Styling process checklist color wise
⇓
1st production report
⇓
End table hourly repot
⇓
End table management report
Working breakdown system:
Preproduction report:
- Approved BOM(Bill of material) sheet.
- Approved trim card.
- Approved sample.
- Approved operation chart.
- Approved measurement sheet.
Cutting Quality:
Cut panel measurement check, 3-pcs sticker match (due to shade), and shrinkage report.
Item confirmation:
Fabric composition, trims card check, embellishment check, and visual inspection.
Input check:
- Bundle check.
- Cut panel measurement check.
- BOM.
- Trim card.
- Sample.
- Operation chart.
- Measurement chart.
Layout:
Garments layout and set-up process mock-up as per buyer requirement.
In-process Quality control:
Every hour check the 7-pcs inline process which affects on traffic light board.
Styling process checking in List color-wise:
Check every process and also check all accessories which match with a trim card.
1st production report:
Measurement check, styling check, Accessories check, and check all kinds of tests.
End table hourly report & End table Measurement report:
1.5 AQL audit. Here if the lot is accepted, send it to the finishing. If a lot failed, it would recheck and re-audit.
Different types of products:
- Polo shirt
- T-shirt
- Jacket
- Sweatshirt
- Long pant
- Short Pant
- Laggings
- Tank Top
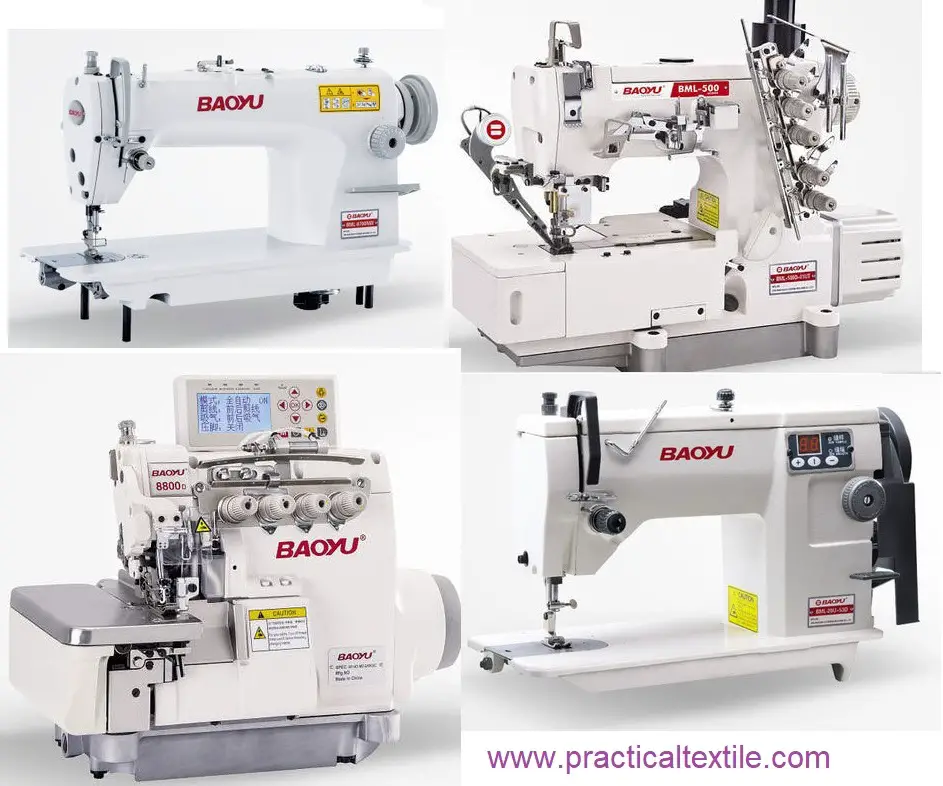
Different types of sewing machines used in the garment industry:
There are thousands of sewing machines available in the garment industry. Some of the basic machines are discussed below:
Machine Name: Lock stitch machine
Brand: Brother
Origin: Japan
Stitch Type: Lock Stitch
RPM: 400-4000
Machine Name: Over Lock Machine
Brand: PEGASUS
Origin: Japan
Stitch Type: Over-edge stitch
RPM: 400-8000
Machine name: Over-edge stitch machine
Brand: JUKI
Origin: Japan
Stitch Type: Over-edge stitch
RPM: 400-7000
Machine Name: Flat Lock Machine
Brand: PEGASUS
Origin: Japan
Stitch Type: Chain stitch
RPM: 2600
Machine Name: Bar Tack Machine
Brand: Brother
Origin: China
SPI: 90-100
Machine Name: Button Hole Machine
Brand: Brother
Origin: China
RPM: 3500
Machine Name: Button Attach Machine
Brand: Brother
Origin: China
RPM: 1500
Machine Name: Feed off the Arm Machine
Brand: Brother
Origin: Japan
RPM: 2860-3450
The function of different sewing machines:
Plain sewing machine:
- Hem joining
- Pocket joining
- Side joining
- Band Tack
- Sideband joining
- Top Seam
- Zipper join
- Zipper top join
- Hood Tuck
Overlock sewing machine:
- The Hood’s outer part join
- The Hood’s inner part join
- The inner & outer parts join
- Servicing join
- Sleeve join
- Front & back parts join
- Hem servicing join
- Side seam
Flatlock machine:
- Top seam
- Armhole top seam
- Front & back join top seam
- Back tape join
Bar tack machine:
- Tuck
The feed of the arm:
- Shoulder top seam
Flatlock cylinder bed:
- Sleeve hem
Button attaching machine:
- Button attach
Eyelet machine:
- Eyelet attach
Basic parts of sewing machine:
- Bobbin:
The bobbin is a cylinder on which a lower thread is wound in a plain machine.
- Bobbin Case:
It holds the bobbin.
- Pressure Foot:
The pressure foot holds fabric flat as it is fed through the machine and stitched.
- Needle Clamp:
It is used to hold & tighten the needle.
- Needle Bar:
It is used to hold the needle.
- Pressure Regulator:
The pressure regulator is used to adjust the pressure foot of the sewing machine.
- Needle take–up:
It takes up the needle to its height position of the sewing machine.
- Tension post:
It gives proper tension to the needle thread of the sewing machine.
- Feed dog:
Feed dog is a critical component of a sewing machine that moves the fabric forward after Sewing.
- Scale:
It controls the density of the stitch per inch.
- Throat plate:
A throat plate is a basic component of a sewing machine where a stitch is formed.
- Spreader:
It is used to give zig-zag stitches.
- Knife lever:
It moves the knife up and down to cut the fabric
- Thread take-up lever:
The thread take-up lever moves up and down, holding the thread following the needle.
- Thread guide: It guides the thread to the needle.
- Looper: It creates a loop of thread in the overlock & flat lock machine.
Types of Needles for a Sewing Machine:
- DBX – Plain machine needle
- DCX – Overlock machine needle
- UYX – Flat lock machine needle
- DPX – Buttonhole needle
- TVX – Feed of the arm machine needle
- UOX – Kansai machine needle
- FLX – Flat seamer machine needle
Different Parts of the Needle:
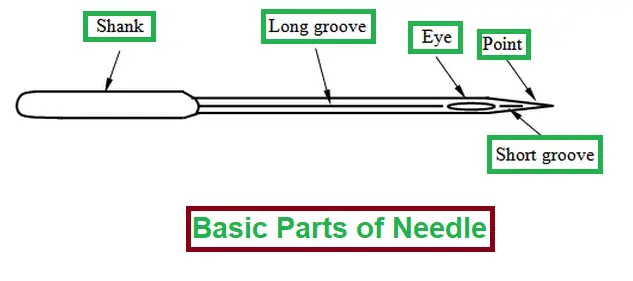
- Shank.
- Long groove.
- Short groove.
- Eye.
- Point.
Needle number used according to fabric:
- Single jersey: 7,9
- Fleece: 9,10,11
- Terry: 9,10
- Pique: 7,9
- Lacoste: 9,10
- Interlock: 9,10
Lay out of basic polo shirt:
- Moon join
- Moon T/S
- Moon Gap Scissoring
- Front and Back part match
- Shoulder joint
- Shoulder T/S & Cut
- Sleeve paring & match
- Sleeve join
- Armhole T/S
- Thread cut & fold
- Placket position mark at body
- Placket fusing
- Placket mark
- Placket O/L
- Placket attach
- Placket Scissoring
- Nose Tack
- Collar servicing & mark
- Collar tack with body
- Collar join with back tape
- Back tape cut & placket fold
- Label position mark
- Back tape close
- Placket scissoring & thread cut
- Lower placket close
- Upper placket 1/16 T/S
- Pattern T/S
- Placket box & thread cut
- Bottom hem
- Check & thread
- Care label make
- Side seam &fold
- Sideband tack & placket inner tack
- Sideband make
- Check & thread cut
- Sleeve hem
- Check & thread cut
- Buttonhole
- Button position mark
- Button attach
- Button insert, Thread cut & fold
Different Types of Stitches:
- Lock stitch:
- Chain stitch:
- Over-edge stitch:
- Tuck stitch:
- Buttonhole:
- Button attach:
- Eyelet attach:
Different types of stitch defects:
Broken stitch: In the middle of Sewing, breaking the thread is called a broken stitch.
Causes:
- Unskilled operator.
- Incorrect machine adjustment.
- If the thread breaks during trimming.
Skip stitch: If the stitch is not locked properly.
Causes:
- Incorrect selection of needle size and thread according to the fabric.
- Incorrect machine adjustment.
- Bad quality sewing thread.
Jam stitch: Double stitches in the same position is called jam stitch.
Causes:
- Unskilled operator.
- Incorrect machine adjustment.
Puckering: After Sewing, if fabric is creased.
Causes:
- Incorrect fabric grain line.
- Improper maintenance of sewing allowance.
Oil spot: Any type of oil mark on the fabric.
Causes:
- Incorrect machine maintenance
- Oil leakage in the machine.
Raw edge: Uncut edges of fabric is called raw edge.
Causes:
- Wrong marking.
- Improper machine adjustment.
- Careless operating system.
Needle Hole: Any type of hole in the fabric due to a broken needle.
Causes:
- Broken needle.
- The wrong needle number was used.
- Careless operating system during the repair.
Mismatch Stripe: Mismatch stripe after Sewing.
Causes:
- Incorrect cutting.
- Improper machine adjustment.
- Unskilled operator.
Dirty Mark: Any type of dirty marks occurred in the fabric.
Causes:
Uncut Thread: Uncut thread after Sewing.
Causes:
- Incorrect adjustment of the auto trimming machine.
- The carelessness of the operator and helper.
- Incorrect thread trimmings part.
Conclusion:
From this article, we have gathered vast knowledge about Sewing Room Management in the Apparel industry. We have learned many things, such as different types of Sewing machines, their functions, different types of faults with their causes and remedies, production techniques, and the overall management system of the sewing section. Officers and workers of the Sewing section were very helpful.
Research link:
- Singer Corporation (redirect from Singer Sewing Machine Company)
- Operations management
You may read some other articles: