Cotton fabric can be dyed with reactive dyes, which are often more durable and fade-resistant than traditional dyes. These dyes have a higher reactivity, so they require less dye per unit area to achieve the desired color. This means that they are also less toxic and less likely to cause allergic reactions. There are several types of reactive dyes, including those that react with ambient light, those that react with other chemicals, and those that undergo photo-bleaching.
Study of Cotton:
Cotton is the most common natural fiber. It is the most popular fiber all over the world. Cotton is the cellulose fiber. Because of its wear comfort, it has become famous all over the world. So the study on dyeing cotton fabric with reactive dye is famous for every learner.
Properties of Cotton:
- Color: Creamy white, yellowish-white.
- Tensile strength: Normally strong fiber. Tenacity- 3-5 gm/den
- Elongation at break: 5-10%
- Elastic recovery: It is inelastic fiber. At 2% elongation ER=74% and at 5% it will 45%
- Specific gravity: 1.54
- Moisture regain%= 8-8.5
- Sunlight effect: It loses strength in sunlight and turns yellow.
- Effect of alkali: It is not damaged by alkali.
- Dissolving: It is dissolved in copper complexes and concentrated (70%) sulphuric acid.
- Water absorbency: 1 gram fiber can absorb 24gm of water.
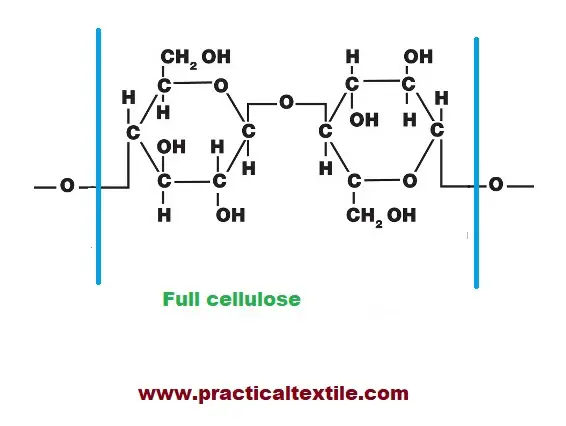
Study of Reactive Dyes:
Reactive dyes are the most usable and popular dyes stuff all over the world because of their good fastness property. it makes the covalent bond to the cellulose.
Properties of reactive dyes:
- Reactive dyes are water-soluble dyes.
- This dye is anionic in nature.
- They have good water and light fastness property.
- Substantively is better.
- It can make a strong covalent bond to the cellulose fiber.
- Need alkaline condition to dye
- A small number of dyes are hydrolyzed during application.
Considering factor dyeing of cotton fabric with reactive dye:
Some influencing factors that are essential for the study of dyeing cotton fabric with reactive dye. are given below-
- PH: Reactive dyeing needs in an alkaline medium. It should be 11.5-11.
- Temperature: Normally at 60’C. But it depends on the brand of reactive dyes.
- The concentration of electrolyte: Depends on the shade%.
- Time: Normally 60min to 90min.
- Liquor ratio: Depends on the fabric property, dye behavior, and Dyeing machine performance.
The general structure of Reactive dyes:
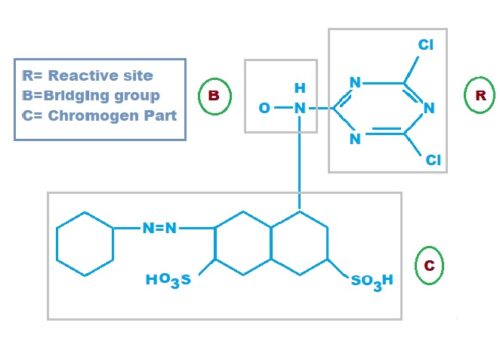
C–B–R= reactive group.
Here,
C= Chromophore (Azo group, Anthraquinone, Phthalocyanine group, Complex group of metal)
B= Bridging Group (Imino, Ethyl & Methyl, Oxide, and Sulphide group)
R= Reactive Group (-Cl, -Br, -SH, -OCH, etc.)
History of reactive dye
Reactive dyeing is a type of textile dyeing in which the dye molecules attach themselves to the fabric fibers by means of chemical reactions. This process was first developed in the early 1800s, and it quickly became the most popular method of dyeing cloth. In reactive dyeing, the dyes are applied to the fabric as a liquid solution, and they then react with the fibers to create a permanent bond.
Why reactive dye is the best dye for cotton?
Reactive dyes are best for cotton fiber because they form a covalent bond with the cellulose molecule in the cotton fiber. This covalent bond is very strong and resistant to washing and fading. Other types of dyes, such as direct dyes, can also be used on cotton fiber, but they are not as durable.
The mechanism for the study on dyeing cotton fabric with reactive dye:
Cellulose+ Reactive dyes= Cellulose–Hydrogen bond–Reactive dyes
There are three basic techniques to consider for the reactive dyeing process. This dyeing mechanism occurs only in the dyeing portion of the dyeing process flow chart. which are given below:
- The attachment of the dye molecule to the surface of the fiber.
- The penetration of dye molecules to the core of the fiber.
- The fixation of dye molecules to the molecular structure of the fiber.
There are three basic parts of the reactive dyeing process which are given below:
- Pretreatment: The process of preparing the fiber to dye. Scouring, Bleaching, and enzyme processes make the fiber prepared for dyeing.
- Dyeing: Colorant material is used here to dye the fiber molecule.
- Aftertreatment: loose dyes are removed here. Dye-fixing chemicals are used here to fix up the dye material. The fiber is also softening here.
A 100% practical usable dyeing process of reactive dye on cotton is given below:
Fabric load
⇓
Scouring and bleaching
⇓
Enzyme if need
⇓
DYEING START
⇓
Leveling 40⁰C
⇓
Runtime 5 minute
⇓
Temperature rise to 80⁰C
⇓
Color dosing 80⁰C 30 minute
⇓
Runtime 15 minute
⇓
Salt dosing 10 minute
⇓
Runtime a10 minute
⇓
Temperature up to 90⁰C, Runtime 20 minute
⇓
Cooling at 60’c (Fabric Check)
⇓
Soda dosing 10% at 15 minute
⇓
Runtime10 minute
⇓
Soda dosing 90% at 25 minutes.
⇓
Runtime 10 minute
⇓
Sample check
⇓
Rise temperature at 80⁰C
⇓
Runtime 10 min
⇓
Sample check
⇓
If ok then BD (Batch drop)
⇓
Normal hot 80⁰C
⇓
Runtime 10min
⇓
Acid wash
⇓
Fixing
⇓
Softener
⇓
Unload
For better understanding complete dyeing with photographs are

Conclusion study on dyeing of cotton fabric with reactive dye:
Cotton is the most popular using fiber, as well as reactive dyes, are also the most popular dyes to use. So the study on dyeing cotton fabric with reactive dye is so important topic.
In conclusion, the study found that dyeing cotton fabric with reactive dye produces high-quality results with good colorfastness. The use of a soda ash fixative also increases colorfastness. The study recommends using a vat dyeing process for the highest quality results.
Research link:
You may read some other articles:
FOR MORE INFO VISIT KNIT DYEING DETAILS